Interactions between MDF and ACT-R
This directory contains examples of ACT-R models converted to MDF. The ACT-R models count.lisp and addition.lisp are based on the ACT-R tutorial.
The scripts count.py and addition.py can be run to create the MDF .json and .yaml files for the given example and execute it using the MDF scheduler.
The below graph represents the basic structure of all ACT-R models in MDF:
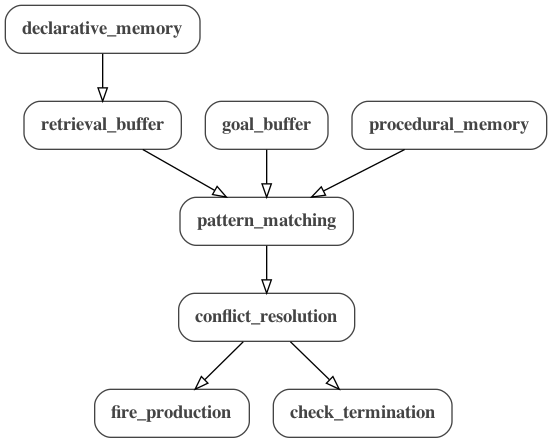
There are also more detailed graphs count.png and addition.png for each example.
Count Model
ACT-R | JSON | YAML | Python Script | Graph
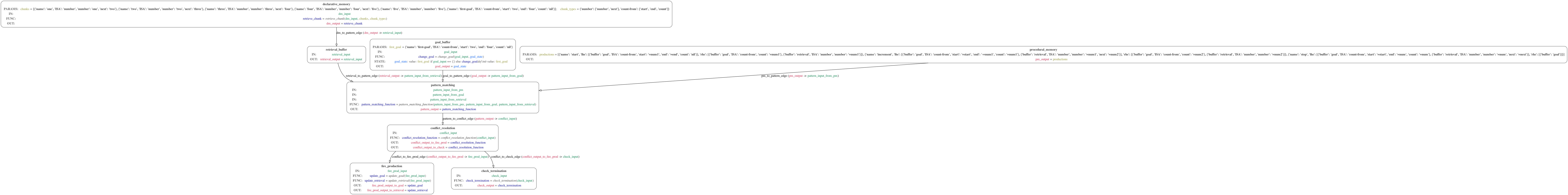
The count model counts from a start value to an end value. The script count.py first reads the original ACT-R model file count.lisp, generates an MDF representation using the MDF ACT-R interface, and outputs the JSON and YAML files. It then executes the MDF model using the MDF scheduler and outputs the final goal set by the model once execution is finished. The final goal has the form:
{'name': 'first-goal', 'ISA': 'count-from', 'start': 'two', 'end': 'four', 'count': 'four'}
In this example, the start value is two, the end value is four, and the final value of count is four, indicating that the model counted from two to four. The start and end values can be modified in line 17 of count.lisp, which sets the initial goal of the model:
(first-goal ISA count-from start two end four)
The script can use any values specified in count.lisp, so the model can be modified and run multiple times in order to test different values. The count graph represents this example.
Addition Model
ACT-R | JSON | YAML | Python Script | Graph

The addition model computes the sum of two numbers. The script addition.py functions identically to the previous example, but uses the addition model instead. The final goal has the form:
{'name': 'second-goal', 'ISA': 'add', 'arg1': 'five', 'arg2': 'two', 'sum': 'seven', 'count': 'nil'}
In this case, the first argument is five, the second argument is two, and the model has calculated the sum, seven. Like the previous example, the arguments can be modified in line 23 of addition.lisp in order to test different values:
(second-goal ISA add arg1 five arg2 two)
The addition graph represents this example.